Current evidence indicates obesity and other metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance are influenced by host genetics and lifestyle. This cascade of ever growing diseases is also associated with low-grade inflammation, as indicated by an
http://c8.alamy.com/comp/BA0KRD/fat–obesity-obese-fat-overweight-torso–teen-england-homer-BA0KRD.jpg https://cbsnews1.cbsistatic.com/hub/i/2015/06/01/c99b61ea-f506-47ce-8cd5-a13aa65b1199/belly-fat-istock000033652758full.jpg

A Low-Carbohydrate, Ketogenic Diet versus a Low-Fat Diet To Treat Obesity and Hyperlipidemia: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Free. William S. Yancy Jr., MD, MHS; Maren K. Olsen, PhD; John R. Guyton, MD; Ronna P. …
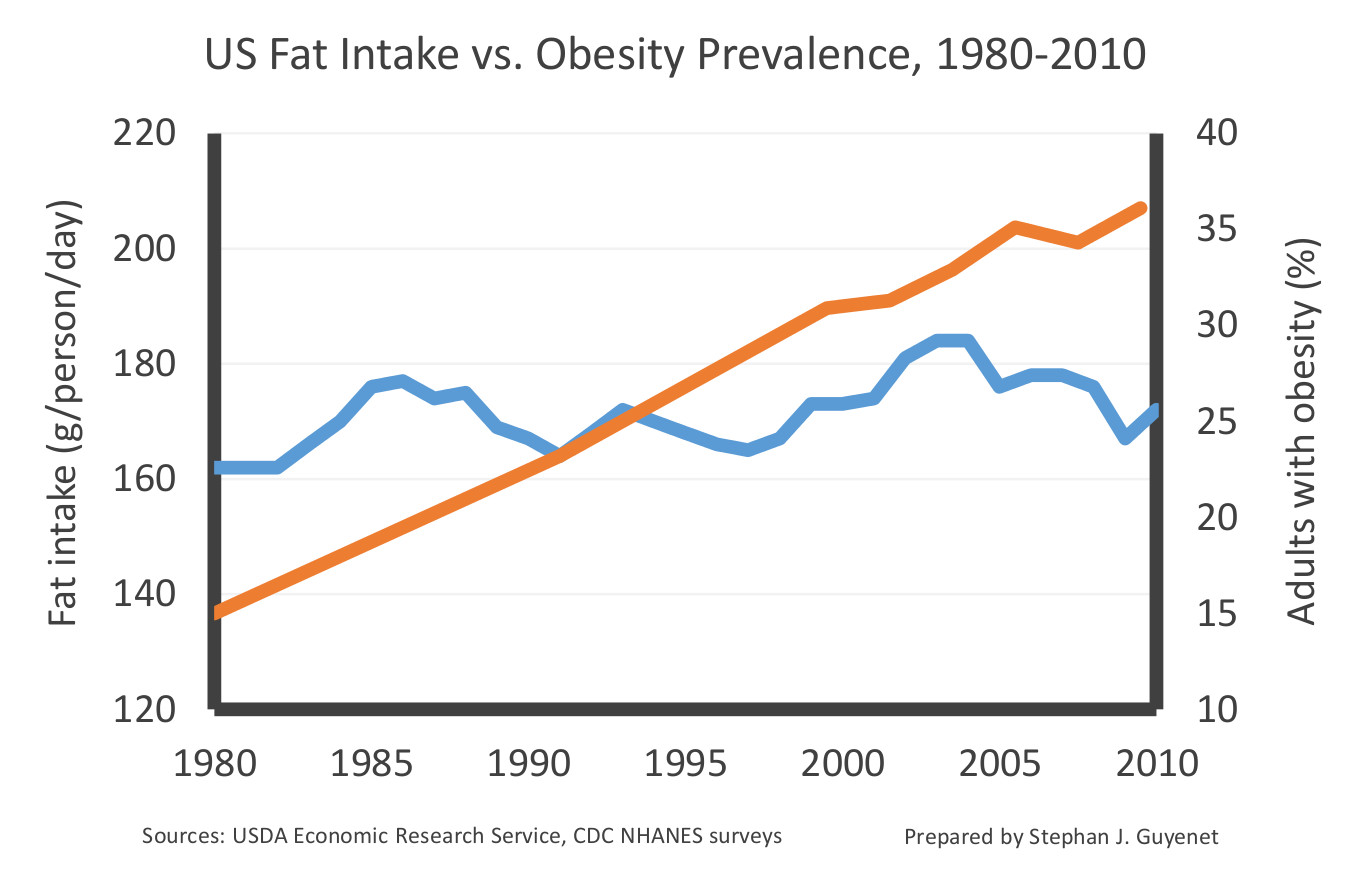
Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat… A Low-Carbohydrate, Ketogenic Diet versus a Low-Fat Diet To Treat Obesity and Hyperlipidemia: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Free. William S. Yancy Jr., MD, MHS; Maren K. Olsen, PhD; John R. Guyton, MD; Ronna P. … Calories, number of hours spent exercising, number of pounds to lose, those who are overweight now have a new number to worry about: a “fat” tax. Adding a high tax on unhealthy food and drinks may help slow the rising rates of obesity, according to a new study published Tuesday in the British http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/content/images/articles/316/316383/obese-woman-s-belly.jpg Current evidence indicates obesity and other metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance are influenced by host genetics and lifestyle. This cascade of ever growing diseases is also associated with low-grade inflammation, as indicated by an Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity, occurs when excessive abdominal fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health.
1. Introduction. Obesity is a contributor to the major causes of global disease burden, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer and diabetes .Both genetic and environmental factors are implicated in obesity: family and twin studies estimate the genetic contribution between 45% to 75% and genome wide association studies (GWAS) implicating loci
http://www.gizmocrazed.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/obese-women.jpg http://dybiz.com/sites_randomblog/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/obese-woman-very-fat.jpg
Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat…

For most people, “fat,” particularly the kind that bulges under the skin, is a four-letter word. It makes our thighs jiggle; it lingers despite our torturous attempts to eliminate it. Too much of it increases our risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes (the most common form of the condition Fat, fat, fat! Would all of our weight loss problems be solved if we just eliminated fat from our diets? Unfortunately, it’s not that simple. We actually need fats — can’t live without them, in fact. Fats are an important part of a healthy diet: They provide essential fatty acids, keep our skin

http://www.who.int/entity/mediacentre/factsheets/WHO_Obesity_Facebook.jpg http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-2kgZmm5Vhj0/VkKiTaV5KnI/AAAAAAAAhPo/ZyU48Wt6Abw/s1600/The%2BAverage%2BLife%2BExpectancy%2Bfor%2BObese%2BPeople.jpg

For most people, “fat,” particularly the kind that bulges under the skin, is a four-letter word. It makes our thighs jiggle; it lingers despite our torturous attempts to eliminate it. Too much of it increases our risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes (the most common form of the condition

Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have a negative effect on health. People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI), a measurement obtained by dividing a person’s weight by the square of the person’s height, is over 30 kg/m 2, with the range 25–30 kg/m 2
Got a big belly? You may be at risk for heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, and cancer. Fat Obesity
Calories, number of hours spent exercising, number of pounds to lose, those who are overweight now have a new number to worry about: a “fat” tax. Adding a high tax on unhealthy food and drinks may help slow the rising rates of obesity, according to a new study published Tuesday in the British
Got a big belly? You may be at risk for heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, and cancer.
1. Introduction. Obesity is a contributor to the major causes of global disease burden, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer and diabetes .Both genetic and environmental factors are implicated in obesity: family and twin studies estimate the genetic contribution between 45% to 75% and genome wide association studies (GWAS) implicating loci
Fat, fat, fat! Would all of our weight loss problems be solved if we just eliminated fat from our diets? Unfortunately, it’s not that simple. We actually need fats — can’t live without them, in fact. Fats are an important part of a healthy diet: They provide essential fatty acids, keep our skin

http://www.fitnessvsweightloss.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Obese-woman.jpg

http://www.returnofkings.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/obesity-2295.jpg Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have a negative effect on health. People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI), a measurement obtained by dividing a person’s weight by the square of the person’s height, is over 30 kg/m 2, with the range 25–30 kg/m 2

http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-twqclUo5vyU/VlEWDvHn_2I/AAAAAAAAbcg/xmdA2oeHsxQ/s1600/Fat%2Bvs.%2Bobesity.jpg
Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity, occurs when excessive abdominal fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health.